What Happened On July 1st?
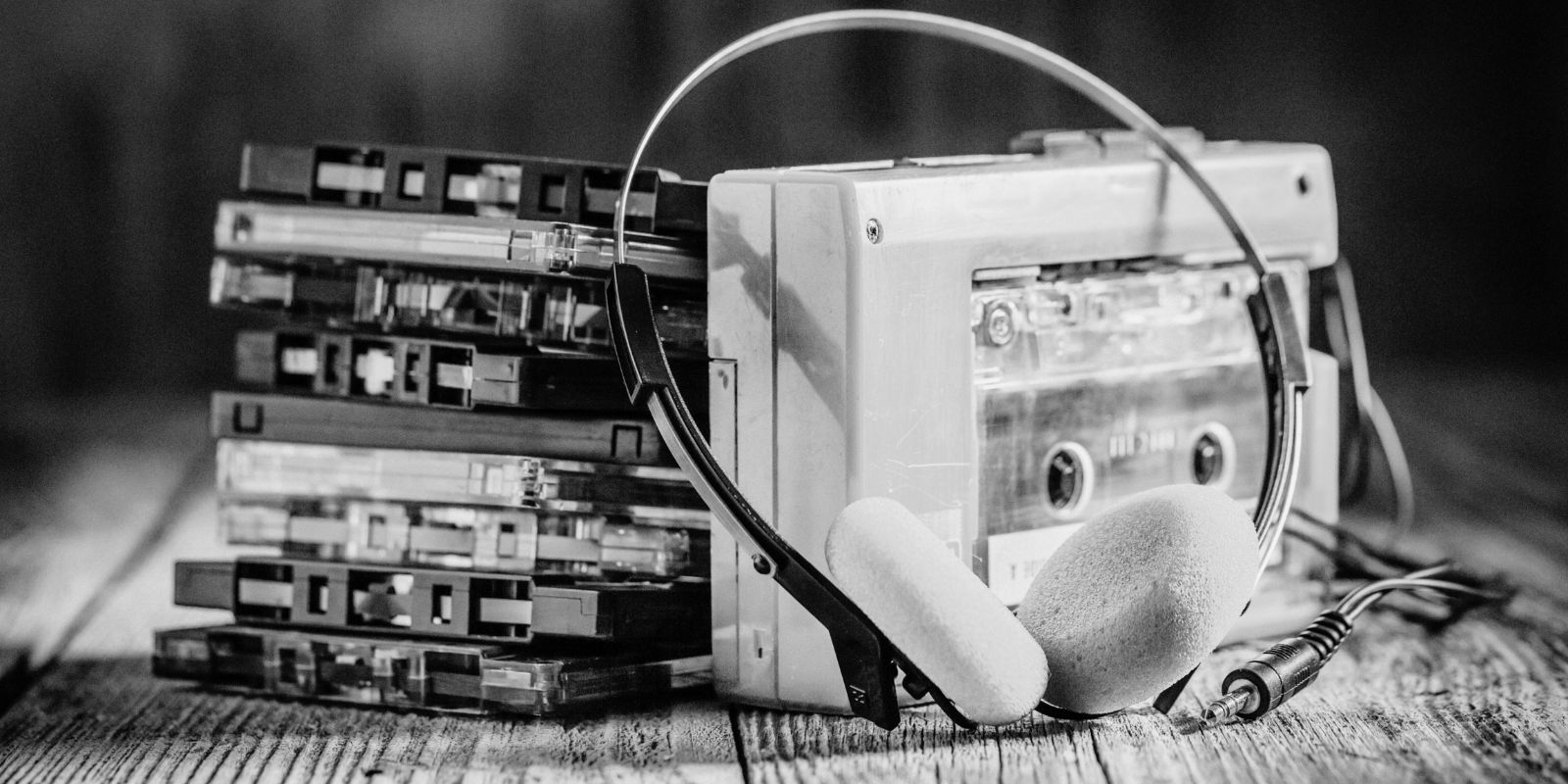
On July 1, 1979, a new device changed the way that people experienced music. The first Sony Walkman, a compact, portable cassette player, hit the shelves in Japan and soon became a global sensation. This small device transformed personal audio consumption and started a new era in the music industry.
Visionary Beats
Sony co-founder Masaru Ibuka envisioned a device that would allow individuals to listen to their favorite music wherever they went without disturbing others. At the time, portable music options were limited, bulky, and lacked high-quality sound. Ibuka aimed to create a lightweight, high-quality device that would change music enjoyment on the go.
Sony’s engineers adapted an existing product, the Pressman, a portable tape recorder for journalists. They removed the recording function and added stereo sound capabilities, creating a new product designed for personal use. The result was a sleek, blue-and-silver device weighing just 14 ounces, with headphones delivering excellent sound quality.
Hitting Play
Sony initially produced a modest 30,000 units, unsure of how the market would respond to this novel concept. However, the Walkman quickly exceeded all expectations. Within the first two months, Sony sold over 50,000 units in Japan alone. The demand for this new device was so high that Sony struggled to keep up with production.
The Walkman’s success was partly due to an innovative marketing strategy. Sony used aggressive advertising campaigns targeting young, active consumers. They showcased people jogging, biking, and skating while enjoying their favorite tunes, highlighting the Walkman’s portability and convenience.
Sony hired young people to walk around busy areas of Tokyo with the device, demonstrating its use and generating buzz. This hands-on approach quickly established the Walkman as a must-have gadget.
Walkman Fever
The introduction of the Walkman changed the way people interacted with music and their surroundings. For the first time, music lovers created their own personal soundscapes, isolating themselves from the noise of the outside world. This newfound freedom resonated with a generation seeking individuality and self-expression.

The Walkman also popularized the concept of “mixtapes.” Users created their own playlists, recording their favorite songs onto blank cassette tapes and sharing them with friends. This practice fostered a deeper connection to music and allowed people to express their personalities through their musical choices.
Soundtrack Of A Generation
The Walkman spurred changes in the music industry, encouraging the production of more portable music formats. Record companies began releasing albums on cassette tapes, which were more convenient for use with the Walkman. The device also contributed to the decline of vinyl records, as consumers favored the portability and durability of cassette tapes.
The success of the Walkman prompted other electronics companies to develop similar products, leading to increased competition and innovation in the portable music market. This era of innovation paved the way for future advancements in personal audio technology, including portable CD players, MP3 players, and, ultimately, digital streaming services.
From Cassette To Disc
The Walkman played a key role in the introduction of the first-ever commercially available compact disc (CD). In 1982, Sony and Philips worked together to launch the CD format, revolutionizing the music industry once again. The Discman allowed users to enjoy this new format on the go, cementing Sony’s reputation as a pioneer in personal audio technology.
The Walkman’s original design included two headphone jacks and a “hotline” button that allowed users to temporarily lower the music volume and speak to a friend. Ibuka believed the Walkman would be used primarily by couples and friends sharing their listening experience. However, it was soon phased out as the device’s popularity grew among solo users.
The Global Influence
The Walkman did more than just change how people listened to music; it became a cultural icon. It influenced fashion trends, as people began carrying their Walkmans everywhere, often incorporating the device and its headphones into their daily attire. The image of someone with headphones on, lost in their own world of music, became a defining symbol of the 1980s.

Music artists and bands also recognized the Walkman’s impact. Many artists considered how their music would sound on portable devices, leading to changes in music production and mixing. The rise of the Walkman also coincided with the explosion of music videos, as the MTV generation embraced the portable music revolution.
Tech Tunes
As the Walkman gained popularity, other electronics companies took note and developed their own versions of portable music players. Brands like Panasonic, Toshiba, and Aiwa introduced similar devices, each trying to capture a share of the booming market. This competition spurred rapid technological advancements and innovations in portable audio.
The evolution of the Walkman saw improvements in battery life, sound quality, and design. Sony released numerous models with various features, such as auto-reverse playback, Dolby noise reduction, and even waterproof versions for sports enthusiasts. These continuous improvements ensured that the Walkman remained a top choice for portable music.
A Digital Takeover
By the late 1990s and early 2000s, digital technology began to overtake analog formats. The introduction of MP3 players and digital music downloads began the decline of cassette and CD-based devices. Despite this shift, the Walkman brand adapted once again, introducing digital music players to compete with emerging products like Apple’s iPod.
Sony’s digital Walkman line included MP3 players with flash memory and hard drives, aiming to maintain the brand’s legacy in the digital age. Although the digital Walkmans never achieved the same iconic status as their analog predecessors, they continued to embody the spirit of portable music innovation.